Copepods confirmed as a nutritious diet for a diverse range of fish

The tiny planktonic larvae of many warmwater marine fish species are not easily reared using conventional cultured prey, rotifers, Brachionus sp., and brine shrimp, artemia sp. The mouths of fish such as groupers, snappers, and marine ornamental species are in many cases too small at first feeding to ingest even small rotifer strains. Such larvae require prey smaller than 100 μm. Furthermore, those larvae that do ingest rotifers often exhibit high mortality and slow growth under intensive culture conditions, indicating their diet is nutritionally deficient.
Against this background, the emerging ability to mass produce small tropical marine copepods under controlled conditions is paving the way to culture a diverse new range of foodfish and ornamental fish species.
Traditional zooplankton culture
Aquaculturists have traditionally used an extensive or “mesocosm” approach to rear small tropical marine fish larvae. In this technique, a mixed population of natural phytoplankton and zooplankton is enclosed in a large outdoor tank, pond, or lagoon, which may be fertilized to boost primary productivity. Fish larvae are then added and allowed to graze on the enclosed plankton. Alternatively, the appropriate plankton fraction can be harvested from the system and administered separately to larvae.
This approach requires only simple rearing facilities and provides the fish larvae with a diverse range of plankton to meet their changing developmental needs. It is therefore useful in locations with limited technical resources, or for newly cultured fish species for which precise dietary requirements are unknown.
Large quantities of marine fish fry and zooplankton biomass are produced using this method, especially in Asia. However, fry output is highly variable, due to the lack of control over plankton abundance, species composition, and physical environmental conditions. In addition, the open nature of mesocosm systems prevents the exclusion of fish pathogens, so serious disease outbreaks are common.
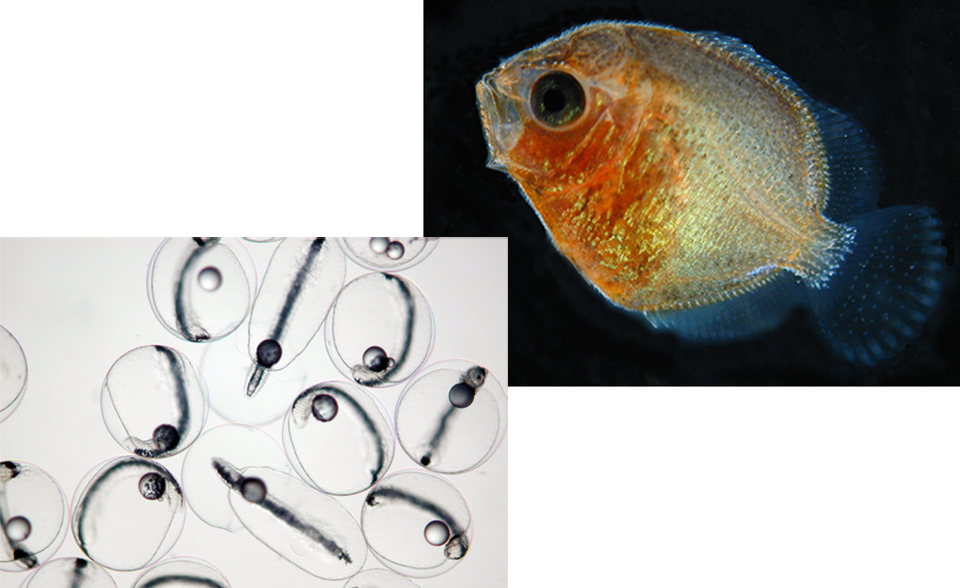

Intensive copepod production
Due to the limitations of the extensive approach, researchers have sought to identify and culture specific zooplankton as prey for small marine fish larvae. Intensive diet production systems require less water volume than mesocosms, provide more consistent output in prey numbers and nutrient composition, and are independent of ambient environmental conditions.
Marine copepods have been the main focus of this work, because they form an important natural component of the larvaes’ diets and have proven effective for culturing difficult-to-rear fish species. In particular, the small naupliar stages of marine copepods offer a suitable-sized prey organism for first-feeding larvae that is rich in highly unsaturated fatty acids and digestible phospholipids. Importantly, copepod nauplii are only a critical dietary requirement during first feeding, after which larvae can be introduced to “conventional” prey, rotifers and artemia.
Culture species
It is essential to consider the diverse life histories of copepods when selecting species to culture. Epibenthic harpacticoid copepods have proven amenable to high culture densities and can be easily maintained on inert diets. However, there are few examples of the successful use of harpacticoid nauplii for first-feeding small planktonic marine fish larvae, perhaps because of the copepods’ association with substrates. Furthermore, research at the Oceanic Institute in Waimanalo, Hawaii, USA, has shown that certain harpacticoid species, such as Euterpina acutiforns, can be detrimental to fish larvae when ingested during first feeding.
By comparison, further Oceanic Institute research funded by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration found that calanoid copepods offer an entirely planktonic prey source and a number of calanoid species. In particular, those belonging to genus Acartia have been successfully used to first feed marine fish larvae. Despite their appropriate size, nutritional content, and behavioral characteristics, however, calanoid copepods are not yet widely used as feeds in intensive marine fish hatcheries because of the low (less than 1 per millileter) culture densities historically attainable.
Paracalanid copepods
A solution to this problem has recently been identified for warmwater fish species, following the discovery that copepods from the family Paracalanidae can be cultured at much higher population densities. These Paracalanid copepods are small – adults are typically less than 500 μm in length and nauplii less than 80 μm. They grow and mature rapidly, and can be easily maintained in captivity using routinely cultured microalgae such as Isochrysis sp., Chaetoceros sp. and Rhodomonas sp.
At the Oceanic Institute, Parvocalanus sp. has been maintained continuously in culture since mid-2001 and confirmed as a nutritious diet for a diverse range of fish, including Lutjanid snappers, jacks (Carangidae), and Pomacanthid angelfish. Indeed, the world’s first captive production of juvenile flame angelfish, Centropyge loricula, was achieved using this diet.
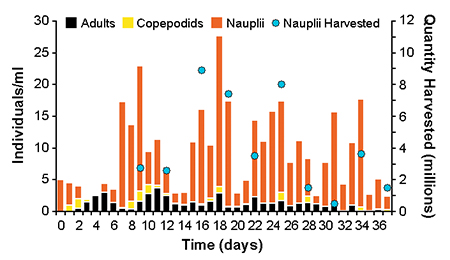
Fig. 1 illustrates Parvocalanus sp. population densities and nauplius harvest quantities for a 400-liter culture tank stocked with nauplii at a density of 5 per millileter and maintained at a temperature of 26 to 28 degrees-C. In this example, adult copepods were first observed two days after stocking and nauplii were harvested from day 9 onwards at three- to four-day intervals. A total of 49 million Parvocalanus sp. nauplii were harvested, equivalent to a mean daily harvest of over 4,000 nauplii per liter.
Conclusion
Intensively cultured Paracalanid copepods represent a valuable new diet for rearing small tropical marine fish larvae under biosecure conditions. Although the harvestable quantities of Paracalanids per unit volume are currently one to two orders of magnitude lower than those achievable with rotifers, it is nonetheless practical to incorporate the copepods as an element of live feed production in intensive marine fish hatcheries due to the critical requirement for nauplii during first feeding. Improvements in system productivity are expected to emerge from ongoing research on copepod diet requirements and husbandry techniques.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the December 2003 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've finished reading the article ...
… we hope you’ll consider supporting our mission to document the evolution of the global aquaculture industry and share our vast network of contributors’ expansive knowledge every week.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year. GSA individual and corporate members receive complimentary access to a series of GOAL virtual events beginning in April. Join now.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
-
Robin J. Shields, Ph.D.
Aquaculture Wales
School of Biological Sciences
University of Wales Swansea
Swansea SA2 8PP, United Kingdom
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Large-scale production system for copepods
The culture of many marine fish species requires the concurrent culture of live feed such as algae and microcrustaceans. The addition of copepods to first feeding often improves survival for small-mouthed species.

Health & Welfare
Advances in intensive copepod production technology
Research at the Oceanic Institute has been successful in overcoming bottlenecks associated with rearing small-mouthed fish larvae by finding a suitable first feed. Early work on the calanoid copepod Parvocalanus crassirostris focused on parameters necessary for successful maintenance of stock cultures.

Aquafeeds
Amino acid requirements in developing marine fish
Most marine fish have pelagic eggs with large pools of free amino acids of fairly constant proportion regardless of species. The amino acids provide energy for metabolism and are an important nutritional asset for growing embryos.

Health & Welfare
Aquamimicry: A revolutionary concept for shrimp farming
Aquamimicry simulates natural, estuarine production conditions by creating zooplankton blooms as supplemental nutrition to the cultured shrimp, and beneficial bacteria to maintain water quality. Better-quality shrimp can be produced at lower cost and in a more sustainable manner.


