Survival, growth and yield were excellent

Polyculture has been practiced using different species mainly for efficiency in utilizing space or feed. The animals selected are generally different in habitat or feeding habits, and can be from the same genus or even different families, but should not be competitors.
Polyculture of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and genetically improved all-male tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) has been carried out successfully on an experimental scale in low-salinity ground water under zero-exchange conditions during winter months to avoid losses due to white spot syndrome virus. Since Pacific white shrimp and black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) have different habitats, feeding habits and tolerance to stocking density, the possibility of utilizing the whole pond water volume in terms of space and feeding for pond efficiency and productivity is promising.
Polyculture study
The authors recently carried out a study to evaluate the polyculture of pacific white shrimp and black tiger shrimp. The L. vannamei were specific pathogen-free (SPF) animals from the Central Pertiwi Bahari (CPB) hatcheries. Also from CPB’s hatcheries, the P. monodon were not SPF, but by polymerase chain reaction tested free of known pathogens prior to stocking.
Culture system
Two earthen ponds of about 0.5 ha were used for each of three stocking treatments: 60 L. vannamei per square meter with 10 P. monodon per square meter, 50 L. vannamei per square meter with 20 P. monodon per square meter, and 40 L. vannamei per square meter with 30 P. monodon per square meter (Table 1).
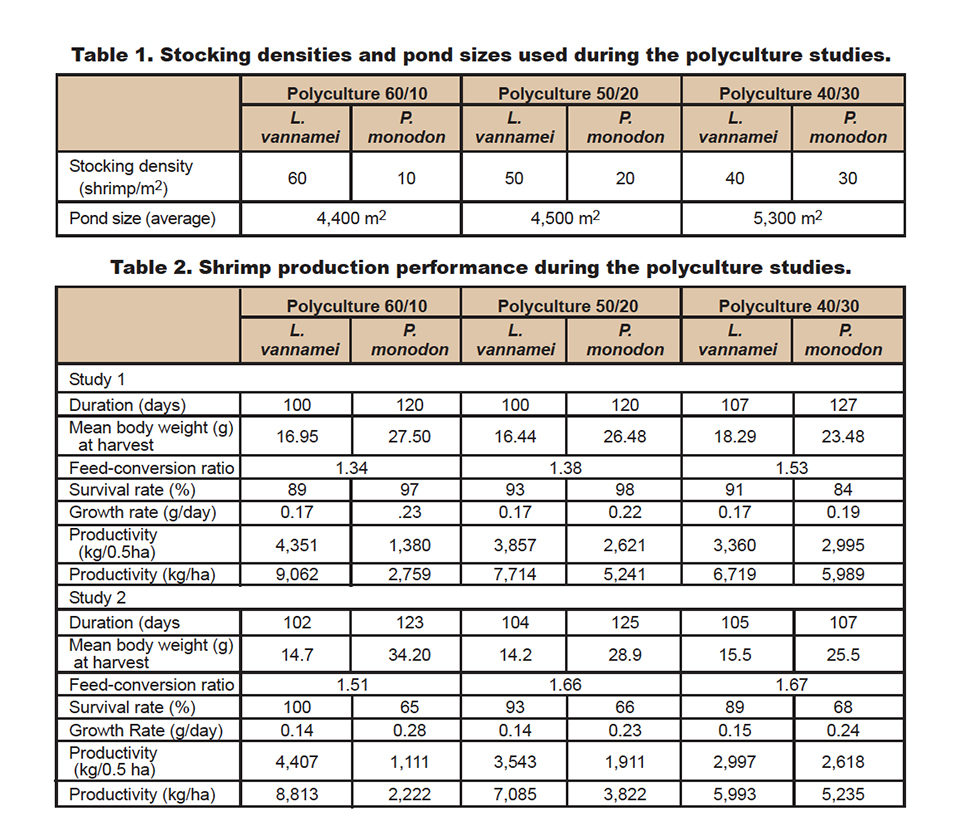
Each pond had paddlewheel aerators to provide circular current flow and accumulate waste in the central areas of ponds, where drains occasionally were used to siphon out sludge. P. monodon postlarvae were stocked directly into the test ponds, while the L. vannamei were first held in a nursery at the farm for 21 days before stocking into the ponds with the P. monodon.
Feeding
Feeding was initially a dilemma, as the two species have different protein requirements, feeding habits, and habitats. Because P. monodon were stocked first, a 38 to 40 percent protein feed was used for the first month. This feed was also used as a booster feed for the L. vannamei. Lower-protein L. vannamei feed with 28 to 32 percent protein was used for the next two months to reduce feed costs.
However, after observing abnormalities in appearance and growth in the P. monodon during routine sampling, high-protein feed was used for the final month. Feed trays were used to monitor feed consumption and adjust rations.
Environmental conditions
Standard environmental parameters – salinity, temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, alkalinity, and bacterial counts – were monitored and found within accepted industry standards.
Production performance
At Central Pertiwi Bahari’s commercial farm ponds, the standards for monoculture of L. vannamei are 9.0 to 16 metric tons (MT) per hectare with 85 percent survival, whereas for P. monodon, standards include 4.0 to 6.0 MT per hectare with 50 percent survival. The resulting productivity performances for both species in the study was promising (Table 2, Fig. 1). Survival, growth and yield were excellent and related to their combination of stocking densities.
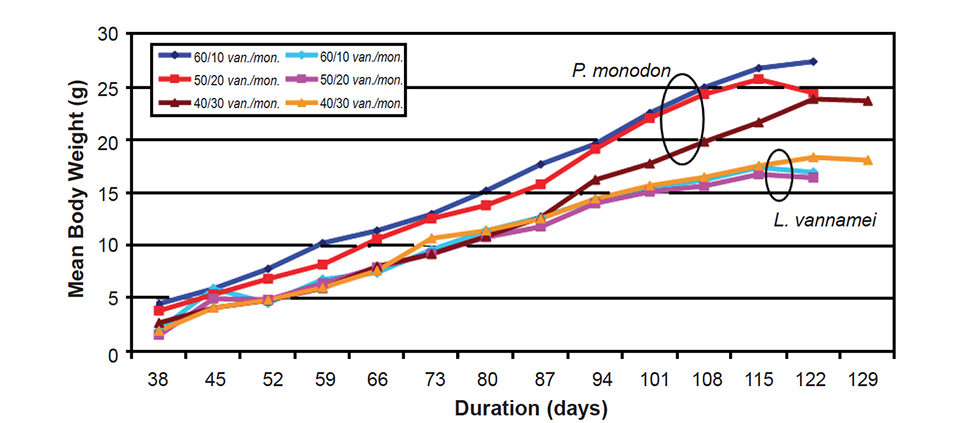
The study was repeated to cover two seasons of the year, with performance found to be almost the same, except for lower survival of P. monodon during the second study. Although the survival was lower, the growth rate was higher and average size was larger.
SPF status

the pond water in terms of space and feeding.
The polyculture of these two species has been variously criticized, as one species is SPF and the other is not. The only concern that resulted from this study was the quality of the P. monodon, L. vannamei survival and other production performance parameters were consistent, possibly due to the animals’ SPF status. However, for P. monodon, these factors varied, especially the survival rate, which reflected on other parameters such as growth and mean body weight. This may have been due to the fact that the animals were not SPF. However, additional studies have been successfully implemented with consistent results.
Stocking densities
All three stocking density combinations, which totaled 70 postlarvae per square meter, resulted in good production performance. Choices regarding which combination to use depend on what farmers want and need. The studies indicated that, if stocked at appropriate densities and times, the two species can coexist and appear to have symbiotic effects on each other’s performance. This has resulted in higher overall pond productivity than in normal monoculture systems.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the October 2005 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've finished reading the article ...
… we hope you’ll consider supporting our mission to document the evolution of the global aquaculture industry and share our vast network of contributors’ expansive knowledge every week.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year. GSA individual and corporate members receive complimentary access to a series of GOAL virtual events beginning in April. Join now.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Nyan Taw, Ph.D.
P. T. Central Pertiwi Bahari
SHS Building, Second Floor
Jl. Ancol Barat, Block A5E No.10
Jakarta 14430, Indonesia -
Saenphon Chandaeng
P. T. Central Pertiwi Bahari
SHS Building, Second Floor
Jl. Ancol Barat, Block A5E No.10
Jakarta 14430, Indonesia -
M. Handoyo Edi
P. T. Central Pertiwi Bahari
SHS Building, Second Floor
Jl. Ancol Barat, Block A5E No.10
Jakarta 14430, Indonesia -
Wayan Suaryanto
P. T. Central Pertiwi Bahari
SHS Building, Second Floor
Jl. Ancol Barat, Block A5E No.10
Jakarta 14430, Indonesia
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Black tiger shrimp domestication advances
The production of early generations of domesticated broodstock in open-environment ponds may have hampered the domestication of black tiger shrimp.

Health & Welfare
Brunei project develops technology for large black tiger shrimp production, part 1
A five-year project was undertaken in Brunei Darussalam to develop advanced technology for the production of large black tiger shrimp. A combination of technologies has enabled efficient production of large-sized black tiger shrimp, which could lead to a resurgence of this species in Asia.

Intelligence
Bangladesh seeks more buck for its ‘bagda’
As more than 80 percent of Bangladeshi shrimp exports already go to EU markets, a consultation meeting involving buyers from the bloc and Bangladesh industry stakeholders and authorities was held at the end of last month in Utrecht, the Netherlands.

Intelligence
Europeans need a new shrimp narrative
Media coverage fuels negative perceptions of farmed shrimp among Europeans. A paper – similar to one on pangasius consumption four years ago – finds the sector is doing too little to rectify ill-founded notions.


