Shrimp capable of feeding on floating feeds within indoor clearwater culture systems

A feeding trial conducted by the authors in 2000 at the Oceanic Institute (OI) in Hawaii, USA tested the effects of extrusion processing on the nutritive value of pelleted feeds for shrimp. In the 12-week trial, part of OI’s shrimp feeds research program supported by the Agricultural Research Service of the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 0.95-gram Litopenaeus vannamei were studied in an indoor, running-water tank system.
Dietary treatments
A total of eight dietary treatments were evaluated:
A. Sinking standard steam-pelleted diet (35 to 37 percent protein), 2.4 mm diameter
B. Floating extruded/spherical agglomerizer system (SAS) diet, 3.2 mm diameter
C. Sinking extruded/SAS diet, 1.6 mm diameter
D. Floating extruded diet, 3.2 mm diameter
E. Sinking extruded diet, 2.4 mm diameter
F. Floating commercial catfish diet (37 percent protein), 2.8 to 3.35 mm diameter
G. Floating commercial trout diet (42 percent protein), 1.5 to 1.8 mm diameter
H. Floating commercial trout diet (45 percent protein), 1.5 to 1.8 mm diameter
Diet A was processed at OI using a pellet mill. Diets B to E had the same feed formulation, but were processed by Extru-Tech Inc. in Sabetha, Kansas, USA, which reground the feed in a mill to pass through a 0.04 (1.0-mm) screen. Moisture was then added to the mashes in a conditioner prior to extruding to 35 to 40 percent moisture. The mashes were extruded with a 1.5-mm screen die.
Extruded 1.5- to 2.0-mm strands of sinking and floating feed were collected and transferred to a spherical agglomerizer system to form two types of feed. The other two sinking and floating diets were extruded with a 2-mm die. In addition to the above OI formulations, three commercial floating feeds were also evaluated.
Experimental setup
Each diet was fed to triplicate groups of shrimp for 12 weeks. Animals were fed by hand to satiation four times daily at 8 a.m., 11 a.m., 2 p.m. and 5 p.m. The water temperature during the experiment ranged 25.1 to 26.2 degrees-C, with a mean of 25.7 degrees-C.
Final weight, feed efficiency
Table 1 shows shrimp growth and feed performance over the experimental period. Treatment E produced the highest mean final body weight of shrimp (8.35 grams), followed by treatments C (8.17 grams), D (7.37 grams), B (7.21 grams), A (7.11 grams), F (3.26 grams), H (3.15 grams) and G (2.93 grams).
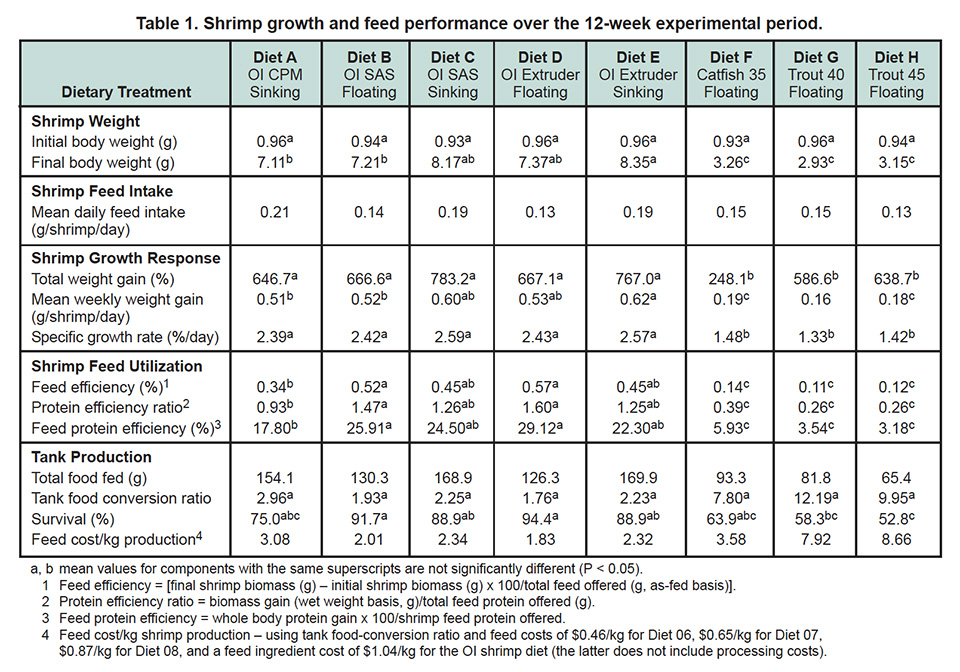
Feed efficiency (final shrimp biomass – initial shrimp biomass x 100 per-feed offered) was highest for treatment D (0.57), followed by treatments B (0.52), C and E (0.45), A (0.34), F (0.14), H (0.12) and G (0.11).
Conclusion
The results of this study demonstrated the beneficial effect on shrimp growth of feeds produced with extrusion processing as compared with conventional steam-pelleted feeds. Moreover, they showed extruded and SAS-processed sinking feeds were superior to floating feeds on the basis of shrimp growth performance, and that the SAS processing method offered no additional advantage compared with extrusion or straight steam pelleting. The results also demonstrated that shrimp were capable of feeding on floating feeds within indoor clearwater culture systems.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the February 2003 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've finished reading the article ...
… we hope you’ll consider supporting our mission to document the evolution of the global aquaculture industry and share our vast network of contributors’ expansive knowledge every week.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year. GSA individual and corporate members receive complimentary access to a series of GOAL virtual events beginning in April. Join now.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
-

Albert G.J. Tacon, Ph.D.
Aquatic Farms Ltd.
49-139 Kamehameha Highway
Kaneohe, Hawaii 96744 USA
Tagged With
Related Posts

Responsibility
Carp polyculture in India
Carp polyculture with other species originally established through government projects has grown in India thanks to the application of advancing technologies and private financial investments.

Aquafeeds
Extrusion processing of aquatic feeds, Part 1
Depending on the extrusion processing conditions and ingredients used, different products such as floating or sinking feed can be produced.

Aquafeeds
Inside the Cargill Aqua Nutrition aquafeed plant in Scotland
Formed in 2015, following Cargill’s acquisition of salmon feed specialist EWOS to complement its own warm-water aquaculture feed business, Cargill Aqua Nutrition produces feed for salmon, tilapia and shrimp in 20 countries around the world.

Aquafeeds
Extruded shrimp feeds reemerge
The process for making extruded shrimp feeds has flexibility to produce diets with a wide range of fat levels, densities, shapes and sizes.

