Courses teach participants to identify seafood problems by smell
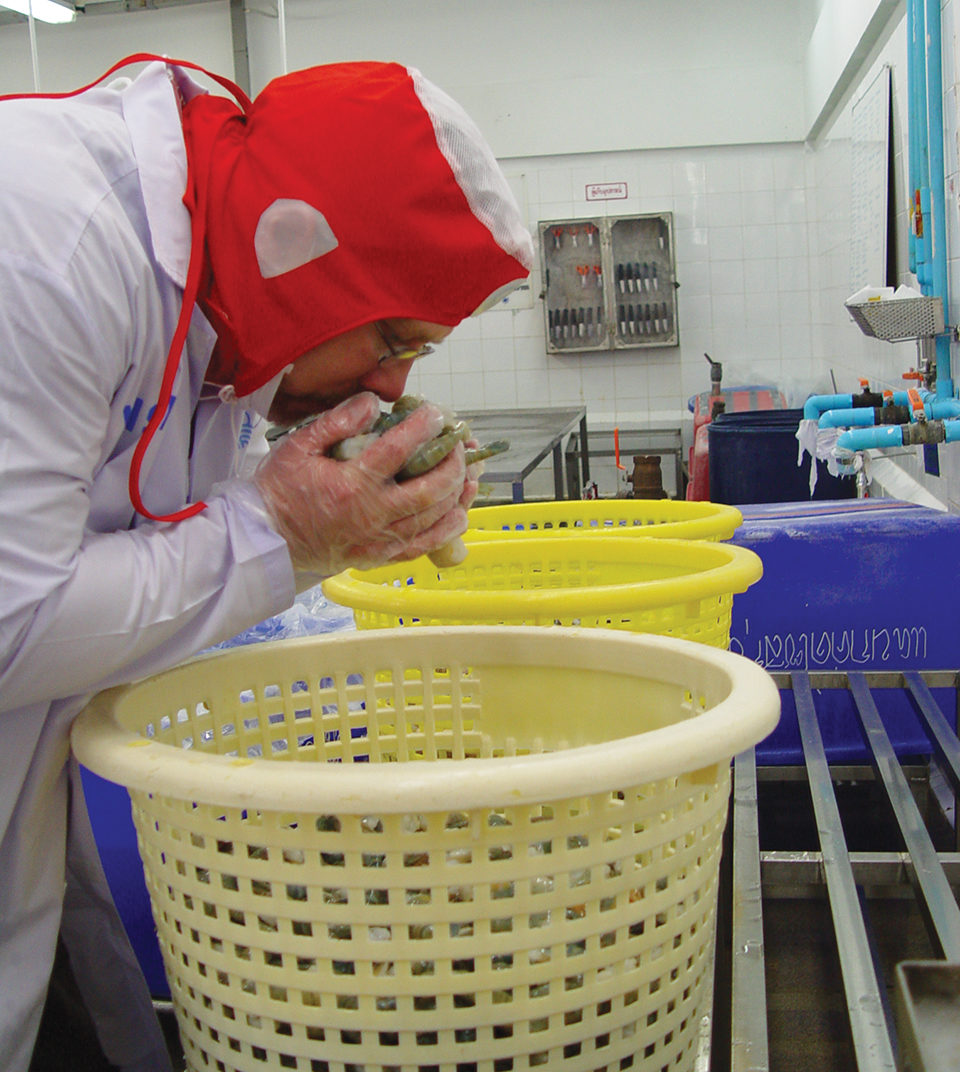

Freshly harvested seafood has a pleasant odor reminiscent of an ocean breeze. But when fish smells, it is past its prime. The odor can be an indication of decomposition that may pose a health hazard to consumers.
When seafood first comes out of the water, the muscle tissue is essentially a sterile product. As it goes through rigor mortis, bacteria and enzymes from the gills and gut cavity begin to multiply and produce compounds that cause a “fishy” smell. Other spoilage bacteria cause fish tissue to soften and further reduce quality.
Inspectors for the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and U.S. Department of Commerce – Seafood Inspection Program (USDC-SIP) use their highly trained noses to determine whether or not imported seafood should enter U.S. commerce.
Sensory training
Sensory evaluation courses can help brokers, processors, regulators, analytical laboratories and retailers involved in supplying, purchasing and inspecting seafood in the U.S. think and smell on par with FDA inspectors. Processors and exporters to the U.S. may be especially interested in understanding the standards applied by the regulatory agencies of countries of origin and the types of odors that can cause their shipments to be rejected.
Sensory training is available through courses offered by universities, trade associations and consultants. Through a variety of teaching methods (blind sampling; sequenced, graded sampling; group discussions) using multiple increments of the same fish with different odor characteristics, participants gain valuable hands-on and “nose-on” calibrating experience in learning how U.S. federal seafood inspectors evaluate seafood products.
Experience shows that it is essential for evaluators to receive periodic training to recalibrate their noses because individuals’ skills tend to drift over time. Some participants become more conservative, while others become more aggressive with their sensory ratings.
Scoring scale
Sensory evaluation courses provide standardized training on different odors and intensities. Participants learn to train their noses to recognize where distinct odors of acceptance and decomposition fall on a 100-point linear scale.
Within seconds, trained sensory analysts can assign a numerical score to identify freshness, spoilage or improper handling. Seafood ranked closest to 100 has the greatest failure qualities, while seafood ranked closest to 0 has the most passing qualities. A score above 50 results in rejection and detention – an expensive consequence for countries that export to the United States, where about 80 percent of the seafood consumed is imported.
Even untrained analysts can easily determine whether a product passes or fails when the odors are closest to 0 or 100. But a challenge occurs even to trained sensory analysts when products exhibit midrange sensory scores of 45 to 55. When sensory quality ratings approach the low to mid-40s, it may not be in the processor’s interest to ship to the U.S. due to the strict guidelines applied by FDA.
Standard descriptors
Standardized seafood species descriptor charts serve as useful guides in sensory evaluation courses (Table 1). These charts provide a range of descriptive terms for odors and intensities varying from “high pass” to “borderline” to “strong fail.” Yet, terms such as “indole” and “yeasty” on the charts may be unfamiliar to participants.
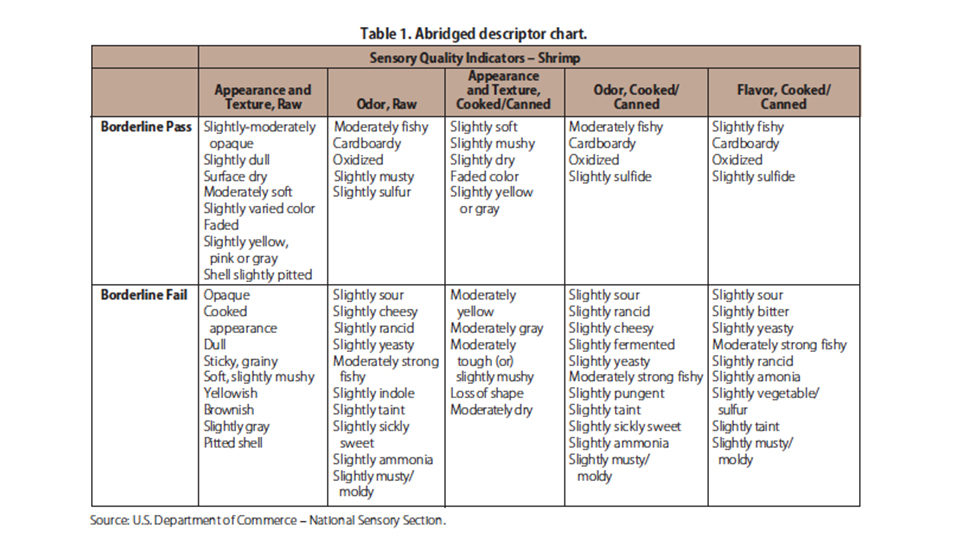
“Cheesy” is an unfamiliar term in Asia because cheese is not a normal product in diets there. However, this same odor can be identified by participants from the Asian region through association with examples that are endemic in their societies. As a result, descriptor charts become dynamic, especially when courses are offered internationally.
In evaluating seafood, feed or background odors can affect the rating of products. Different wild-caught and farm-raised fish and shellfish emit unique odors. It is also critical to know the sources of products when conducting sensory evaluations. A product can exhibit an odor that some mistake as decomposition but that is only a feed odor or something else natural to the species.
Sample preparation
Sensory course demonstration samples are intentionally spoiled via a controlled “spoilage run” to reach a certain quality level on the linear scale.
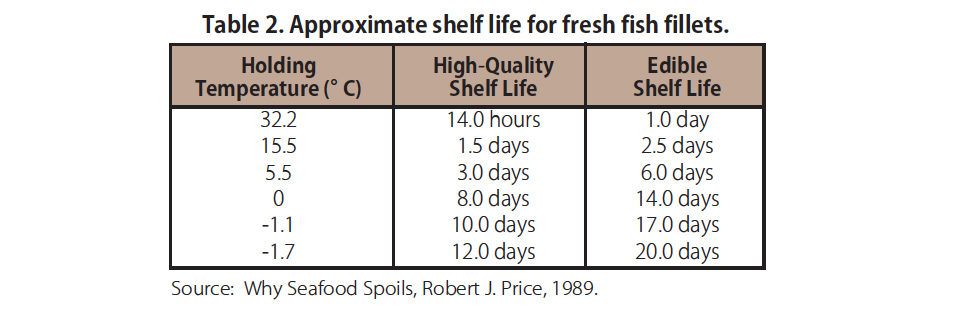
In preparing course samples, sensory experts start with the freshest, highest-quality seafood available and capture the essence of this quality through freezing or canning, The product is then intentionally subjected to time and temperature abuse in order to package varying stages of decomposition for demonstration at the course. As shown in Table 2, the process can take days. Simulations of how the seafood would have spoiled in the real world are also applied.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the September/October 2008 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've finished reading the article ...
… we hope you’ll consider supporting our mission to document the evolution of the global aquaculture industry and share our vast network of contributors’ expansive knowledge every week.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year. GSA individual and corporate members receive complimentary access to a series of GOAL virtual events beginning in April. Join now.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Pamela D. Tom
University of California – Davis
Sea Grant Extension Program
Food Science and Technology Department
1 Shields Avenue
Davis, California 95616 USA[117,100,101,46,115,105,118,97,100,99,117,64,109,111,116,100,112]
-
James Barnett
United States Food and Drug Administration
National Seafood Sensory Expert – Retired
Marysville, Washington, USA
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Aquamimicry: A revolutionary concept for shrimp farming
Aquamimicry simulates natural, estuarine production conditions by creating zooplankton blooms as supplemental nutrition to the cultured shrimp, and beneficial bacteria to maintain water quality. Better-quality shrimp can be produced at lower cost and in a more sustainable manner.

Health & Welfare
Extensive wrasse use keys up ‘cleaner fish’ conservation questions
Few could argue that a reduction in sea lice-fighting chemicals isn't a win for the fish and for the environment. The downside, however, is that increasing numbers of cleaner fish are being caught for use on salmon farms.

Responsibility
Retrofitting shrimp farms to recirculating systems
Several large shrimp farms in Latin America, originally built to operate using significant, flow-through water exchange with the surrounding environment, have been retrofitted to a recirculating operation mode. This modification provides numerous benefits, including improved biosecurity.

Health & Welfare
Rapid on-site diagnostic tool for AHPND management
To help minimize economic losses caused by acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease, timely detection of its pathogenic Vibrio etiological agent plays a critical part in disease management. A portable device with accompanying polymerase chain reaction assays can quickly identify the AHPND markers in shrimp, water, live feed or other sources.


